Remember the excitement of watching your first 3D movie? The content popped out into a new surreal dimension creating never experienced before. Earlier, 3D movies could only be enjoyed in a cinema and very few movies were produced. As things progressed, the demand skyrocketed and today we have a plethora of 3D content available with new titles being launched at regular intervals.
This rise in demand led to the integration of 3D technologies in TVs, projectors and gaming consoles for consumer applications. To enjoy 3D content at home, you need a compatible projector/TV/display, media player, optimized video content and special 3D glasses. When considering a purchase of a 3D TV or Projector, people often neglect to research what type of 3D technology their prospective purchase uses.
At Ooberpad, we thought it would be a good idea to break-down the two popular typed 3D glasses technologies available. Here, we give you a run-down on what each technology is called and what they do to produce a 3D image.
How does 3D in home theatres work?
Before we go ahead, it is a good idea to understand how 3D viewing in achieved in home theatres. 3D TVs and Video Projectors work by accepting an incoming 3D signal that is encoded by the content provider. This can be sent in several different ways. The TV or projector has an internal decoder that can translate the type of 3D encoding used. It displays the left and right eye information on the TV or projection screen in such a way that it appears to look like two overlapping images that look slightly out of focus.
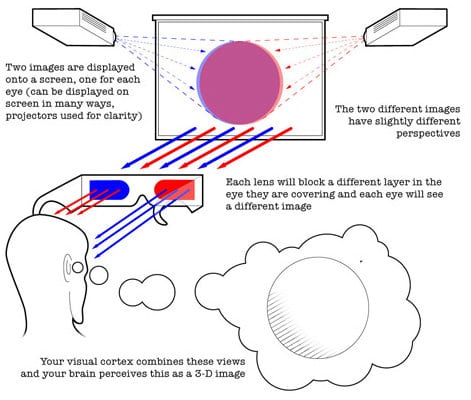
One image is intended to be seen only by the left eye, while the other image is intended to only be seen by the right eye. In order to view this image properly, the viewer must wear glasses that are specially designed to receive the separate images and pass them properly to the left and right eye. 3D glasses work by providing a separate image to each eye. The brain combines the two overlapping images into a single image, which appears to be in 3D.
Types of 3D Glasses
There are two popular types of 3D glasses – Passive Polarized & Active Shutter. Both achieve their 3D visuals in a different way. Here we look at each type and also explain the pros and cons of each technology.
Passive Polarized Glasses

These glasses look and wear much like sunglasses and require no additional power to work. They usually have enough front space to place over existing eyeglasses for those that need to. These type of glasses are inexpensive to manufacture and are priced depending on the frame style such rigid vs flexible, plastic vs metal and so on.
| Pros of Passive Polarized 3D Glasses | Cons of Passive Polarized 3D Glasses |
|
|
Active Shutter Glasses
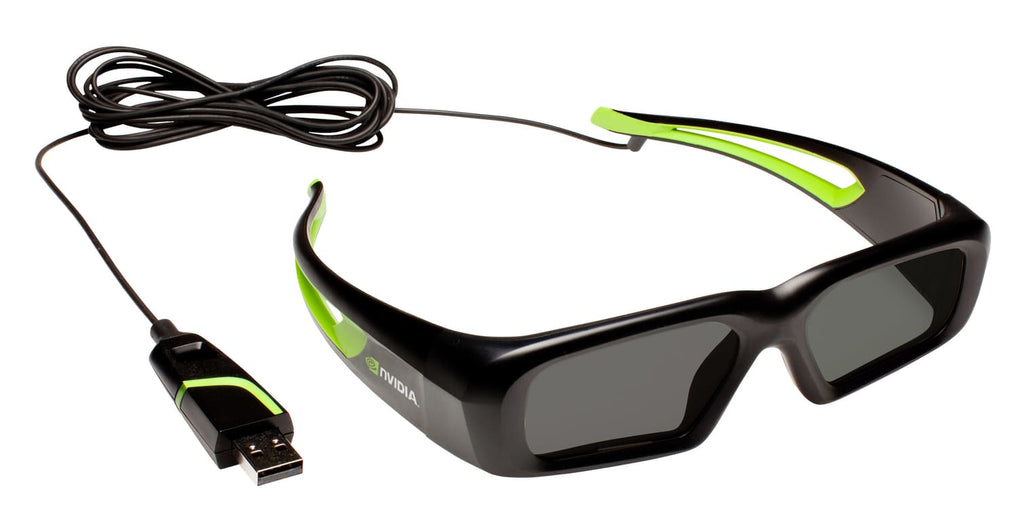

These glasses are slightly bulkier than passive glasses since they have batteries. Some use watch batteries while others provide built-in rechargeable batteries. It also has an on/off button and a transmitter that syncs the rapidly moving shutters for each eye with the onscreen display rate. These type of glasses are also more expensive than passive polarized glasses. The price is higher as it a better technology with added active electronic components.

| Pros of Active Shutter 3D Glasses | Cons of Active Shutter 3D Glasses: |
|
|
Depending on which brand and model TV or video projector you buy, will determine which type of glasses (passive polarized or active shutter) you will be required for use with that TV or video projector. For example, LG 3D-enabled require Passive Glasses, while some Sony TVs required Active Shutter glasses, and some require Passive. All consumer-based video projectors (either LCD or DLP) require the use of Active Shutter glasses. In a nutshell, passive 3D offers better price, weight, size and anti-flickering, but active 3D is still the go-to for outright image quality details.
If you’re looking to buy a projector in India, Ooberpad has a curated collection of high-quality projectors for home theatres, offices, educational institutions at the best price online. Browse our collection below.









